Hours of Instructional Activity Equivalents (HIA) for Planning Instruction
Face-to-face, online and hybrid courses all have the same credit hour requirements for students. The information here will provide Penn State faculty and instructional designers with the means to make general estimates of student learning time in online and blended courses and will help answer the question of “is there too much/not enough” in the course.
Expectations and Terminology
Penn State credit hours and weekly expectations
Time Equivalencies
Time estimations for instructional and learning activites
Tools and Examples
HIA blank templates and examples (Basic and Detailed)
Expectations and Terminology
The Code of Federal Regulations 34 CFR § 600.2 provides the following definitions used to determine institutional eligibility to participate in programs offered by the Higher Education Act of 1965, including participation in Title IV federal financial aid programs. Compliance with the federal requirements also ensures compliance with our institutional accrediting agency, the Middle States Commission on Higher Education (MSCHE).
Distance Education
Education that uses one or more of the technologies [specified in 34 CFR § 600.2]…to deliver instruction to students who are separated from the instructor or instructors and to support regular and substantive interaction between the students and the instructor or instructors, either synchronously or asynchronously.
Correspondence course
A course provided by an institution under which the institution provides instructional materials, by mail or electronic transmission, including examinations on the materials, to students who are separated from the instructors. Interaction between instructors and students in a correspondence course is limited, is not regular and substantive, and is primarily initiated by the student. If a course is part correspondence and part residential training, the Secretary considers the course to be a correspondence course. A correspondence course is not distance education.
If the regular and substantive interaction requirements for distance education are not met, MSCHE could determine courses/programs are being delivered via correspondence, rather than distance education, and Penn State’s institutional accreditation does not cover instruction via correspondence courses.
Regular interaction
Regular interaction includes substantive interactions between a student and an instructor or instructors on a predictable and scheduled basis prior to the student’s completion of a course or competency. Regular interaction entails
- providing the opportunity for substantive interactions with the student on a predictable and scheduled basis commensurate with the length of time and the amount of content in the course or competency,
- monitoring the student’s academic engagement and success, and
- ensuring that an instructor is responsible for promptly and proactively engaging in substantive interaction with the student when needed on the basis of such monitoring, or upon request by the student.
Substantive interaction
Substantive interaction is engaging students in teaching, learning, and assessment, consistent with the content under discussion, and includes at least two of the following:
- providing direct instruction;
- assessing or providing feedback on a student’s coursework;
- providing information or responding to questions about the content of a course or competency;
- facilitating a group discussion regarding the content of a course or competency; or
- other instructional activities approved by the institution’s or program’s accrediting agency.
Credit hour
Credit hour is defined by the U.S. Department of Education (USDE) as an amount of student work defined by an institution, as approved by [the institutional accrediting body, which for the University is the Middle State’s Commission on Higher Education (MSCHE)] or state approval agency, that is consistent with commonly accepted practice in postsecondary education and that reasonably approximates not less than
- One hour of classroom or direct faculty instruction and a minimum of two hours of out-of-class student work each week for approximately fifteen weeks for one semester, or the equivalent amount of work over a different period of time, or
- At least an equivalent amount of work as required in (i) of this definition for other academic activities as established by the institution, including but not limited to laboratory work, internships, practica, studio work, and other academic work leading to the award of credit hours; and permits an institution, in determining the amount of work associated with a credit hour, to take into account a variety of delivery methods, measurements of student work, academic calendars, disciplines, and degree levels.
Academic engagement
Academic engagement is defined as active participation by a student in an instructional activity related to the student’s course of study which includes but is not limited to:
- attending a synchronous class, lecture, recitation, or field or laboratory activity, physically or online, where there is an opportunity for interaction between the instructor and students;
- submitting an academic assignment;
- taking an assessment or an exam;
- participating in an interactive tutorial, webinar, or other interactive computer-assisted instruction;
- participating in a study group, group project, or an online discussion that is assigned by the institution; or
- interacting with an instructor about academic matters; and
- does not include, for example, living in institutional housing; participating in the institution’s meal plan; logging into an online class or tutorial without any further participation; or participating in academic counseling or advisement.
Hybrid Course Classification @ Penn State
All hybrid courses must be classified for the Office of Student Aid to report enrollment mode to the Pennsylvania Higher Education Assistance Agency (PHEAA) for students awarded the PA State Grant. While only undergraduate students are eligible for the PA State Grant, all hybrid courses including master’s level courses must be coded with the proper hybrid classification.
University Senate Policy 42-23 Credit Requirements by Type of Instruction
- For the typical student, a minimum of forty-five (45) hours of work planned and arranged by the University faculty is required to gain 1 credit. 3 credits require 135 hours of instructional activity (HIA).
- The typical distribution of student learning time is approximately one-third instruction and two-thirds outside preparation.
- One (1) PSU credit = 45 Hours of Instructional Activity (15 hours EIA + 30 hours ELA)
- Two (2) PSU credits = 90 Hours of Instructional Activity (30 hours EIA + 60 hours ELA)
- Three (3) PSU 3 credits = 135 Hours of Instructional Activity (45 hours EIA + 90 hours ELA)
| Instruction time (1/3 of total time) |
Outside preparation time (2/3 of total time) |
| Activities that are typically instructor led, guided, or facilitated such as group discussions, field trips, and lectures. | Activities that students actively participate in such as reading, writing, and analyzing. |
|
Also referred to as:
|
Also referred to as:
|
Weekly Expectations Based on Semester Length and Credits
3-Week Course
| # Credits | Total Instruction Time (in hours) |
Total Outside Preparation (in hours) |
Weekly Instruction Time (in hours) |
Weekly Outside Preparation (in hours) |
| 1 | 15 | 30 | 5 | 10 |
| 2 | 30 | 60 | 10 | 20 |
| 3 | 45 | 90 | 15 | 30 |
5-Week Course
| # Credits | Total Instruction Time (in hours) |
Total Outside Preparation (in hours) |
Weekly Instruction Time (in hours) |
Weekly Outside Preparation (in hours) |
| 1 | 15 | 30 | 3 | 6 |
| 2 | 30 | 60 | 6 | 12 |
| 3 | 45 | 90 | 9 | 18 |
8-Week Course
| # Credits | Total Instruction Time (in hours) |
Total Outside Preparation (in hours) |
Weekly Instruction Time (in hours) |
Weekly Outside Preparation (in hours) |
| 1 | 15 | 30 | ~1.875 | ~3.75 |
| 2 | 30 | 60 | ~3.75 | 7.5 |
| 3 | 45 | 90 | ~5.625 | ~11.25 |
12-Week Course
| # Credits | Total Instruction Time (in hours) |
Total Outside Preparation (in hours) |
Weekly Instruction Time (in hours) |
Weekly Outside Preparation (in hours) |
| 1 | 15 | 30 | 1.25 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 30 | 60 | 2.5 | 5 |
| 3 | 45 | 90 | 3.75 | 7.5 |
15-Week Course
| # Credits | Total Instruction Time (in hours) |
Total Outside Preparation (in hours) |
Weekly Instruction Time (in hours) |
Weekly Outside Preparation (in hours) |
| 1 | 15 | 30 | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 30 | 60 | 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 45 | 90 | 3 | 6 |
Time Equivalencies for Instructional Activities
The term “equivalent instructional activity” (EIA) is synonymous with “in-class” and “direct faculty instruction” particularly in a residential or blended course. One important point is that the EIA is not the amount of time that faculty spend teaching the course but rather the amount of time a student would be engaged in this faculty-directed activity. Methods such as discussion boards, exams, and chats can serve as instructional time. However, logging on constitutes neither active faculty teaching nor active student learning.
The term “equivalent learning activity” (ELA) is synonymous with “student work” and includes all assignments or other academic activities required to be completed outside of instructional time. Student work may include reading, studying, writing, completing worksheets, research, etc.
The following table provides estimated equivalencies for the amount of time it will take to complete instructional and learning activities. In some cases, the instructional time and learning activity time will need to be combined to find the total hours for a given assignment.
| Activity | Hours of equivalent instructional activity (EIA) | Hours of equivalent learning activity (ELA) | Notes |
| Blog entries (public) | ½ hour per page | 1 post equals ½ hour |
Students’ opportunity to apply learned concepts or for reflection on learning experiences; To be shared with instructor and/or classmates for thoughtful analysis, feedback and assessment. |
| Journal entries (private) | ½ hour per page | 1 post equals ½ hour |
Students’ opportunity to apply learned concepts or for reflection on learning experiences; Not to be shared with other classmates. |
| Discussion activities | 1 – 3 hours per activity |
|
Instructor-guided or mediated threaded discussion that directly relates to course objectives and which has specified time frames, expectations for participation, and thoughtful analysis. |
| Case study and analysis | 1 – 3 hours | 1 hour equals 1 hour | In-depth analysis requiring utilization of higher order analytical skills which relate to course objectives and is shared with instructor and/or classmates for feedback and assessment. |
| Problem solving scenarios | 1 – 3 hours | 1 hour equals 1 hour | In-depth analysis requiring utilization of higher order thinking and analytical skills which relate to course objectives that may/may not be shared with instructor and/or classmates for feedback and assessment. |
| Synchronous communication | 1 hour equals 1 hour | 1 hour equals 1 hour |
Examples:
|
| Tours and field trips, including virtual | 1 hour equals 1 hour | 1 hour equals 1 hour | Students participate as individuals or in groups in analyzing an activity & preparing a paper or presentation, to be shared in whole or in part with instructor and/or classmates. |
| Group projects | 1 – 3 hours per week for duration of project | 1-10 hours per week, depending on project objective, deliverable, and duration |
Examples:
|
| Guided or service learning projects | 1 – 3 hours per week for duration of project | 1 – 10 hours per week, depending on project objective, deliverable, and duration |
Examples:
|
| Laboratory, Virtual Laboratory and Lab Reports |
|
Creating and conducting of experiments (kit or simulated) and writing of laboratory report(s). Potential to have student collaboration with reviewing and responding via posting of reports as a team or as class discussion. | |
| Lecture activities including lecture notes | 1 hour equals 1 hour | 30 minutes per page of notes | Notes in response to video and lecture |
| Media projects: Podcast | 1 hour equals 1 hour | 10 – 12 minutes equals ½ – 3 hours of instruction depending on production value | For every minute of a completed podcast project, several minutes will be required for production. The variation is dependent upon format: interview/informal with minimal post-production to creative/high production with potential special effects / field recording. |
| Media projects: Video | 1 hour equals 1 hour | 3 – 5 minutes of minimal production value video equals 1 – 3 hours of instruction | For every minute of a completed video project, several minutes will be required for production. The variation is dependent upon format: interview/informal with minimal production value, remix/mash-up, or creative/high production with potential special effects / field recording. |
| Online Quizzes | 1 hour test equals 1 hour | 1 hour test equals 1 hour | Opportunity for instructor to assess students’ subject knowledge and provide feedback on students’ progress. |
| Peer Review / Assessment | Up to 1 hour per page for review of peer papers | Student review of peer assessment and follow up response post/email to student/teacher equals ½ – 2 hours of instruction | Review of peer papers |
| Reflection Paper |
|
½ hour per page | Informal writing in reaction to a reading, video, quote, or questions from professor |
| Research Paper |
|
2 hours per page | Research and writing of a formal research paper. |
| Readings | n/a |
|
Examples:
|
Tools and Examples
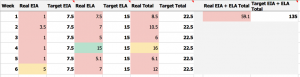
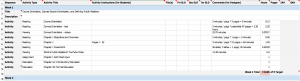
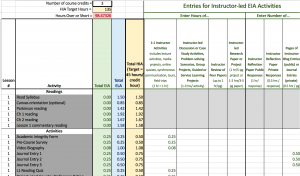
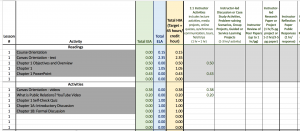
For a generalized overview of the HIA across the whole course, a web app has been developed that lets you quickly add, adjust, and remove activities. For a more specific, week-by-week calculation of HIA, BASIC and DETAILED HIA calculation spreadsheets have been developed. In addition to the blank template for each version, there are example versions as applied to specific courses. Any of these can be downloaded and customized to meet the needs of specific individuals and units. The examples demonstrate various ways that instructional designers and faculty have used information about hours of instructional activity (HIA) with their courses. There is no one way to utilize these HIA resources but rather what is included can serve as a guideline for designing course assignments.
General Estimation and Course HIA Overview
The Hours of Instructional Activity Estimator
The HIA Estimator web app is a quick and easy tool to estimate how many hours of student learning time are involved in a course plan by providing instant visual feedback and hourly breakdowns based on the activities added to it.
BASIC HIA Spreadsheet Tool
BASIC HIA Tool - Applied to HDFS course
BASIC HIA Tool - Applied to MKTG course
DETAILED HIA Spreadsheet Tool
DETAILED HIA Tool - Applied to ENGR course
DETAILED HIA Tool - Applied to MKTG course
These resources were initially produced through the efforts of the Penn State Online Faculty Engagement Subcommittee during the 2017-18 academic year and subsequently updated during the Fall 2021 semester. The material is intended to serve as guidelines and to facilitate discussion around course activities. Except where otherwise noted, this content is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License